Sustainability has become a buzzword in recent years, inspiring initiatives, research, and discussions across industries and governmental bodies. But what does the term "sustainable practice truly mean, and why should we care about it?
At its core, sustainable practices refer to practices that meet our present needs as a society but do not compromise the ability of future generations to meet theirs. For instance, an unsustainable practice is the reliance on a finite fossil fuel supply for energy generation as even though it meets our current needs, this supply will unlikely last for future ones.
As such, implementing sustainable practices is all about creating a future that others can also create a future in.
In this article, we will be focusing on the topic of food sustainability, understanding its importance and how it also relates to other forms of sustainability.
Most importantly, we will also learn about how we can do our part in the efforts to contribute to a sustainable future in our very own homes. So if this interests you, read on to find out more!
PS: In another article, we also shared how we could implement sustainable practices in our own homes, beginning in the kitchen with the repurposing of vegetable scraps. Check it out here!
What is Food Sustainability?
Before we learn how we can contribute to food sustainability, we first have to understand what it means.
When we look at food sustainability, it is crucial to understand that it does not just deal with food alone, but all the other factors surrounding it – ranging from how they are produced and processed to how they are then packaged and distributed.
Food sustainability is thus an all-encompassing term that consists of almost anything under the sun food-related and can be summarised as:
Practices and systems involved in the management of the production, distribution, consumption, and disposal of food to ensure their social, economic and environmental viability.
"According to the United Nations (UN), a sustainable food system can be defined as a food system that delivers food security and nutrition for all – a goal which has not yet been met by our current food system."
Why is Food Sustainability important?
So why should you care about food sustainability?
The importance of food sustainability lies in its relation to other forms of sustainability and its far-reaching impacts on societies as a whole. With current food systems being neither efficient nor sustainable, they have become insufficient in ensuring food security globally, with almost 10% of our global population (~735 million) facing chronic hunger in 2022.
"As the global population continues to increase to an expected 10 billion by 2050, it's not difficult to imagine how much further the issue of food insecurity will be exacerbated by then."
Additionally, current efforts to reduce world hunger (Sustainable Development Goal: Zero Hunger) by 2030 have proven to be insufficient, prompting the need for increased efforts to meet the goal – with at least 660 million people still expected to live in famine states by 2030.
While efforts are being made to reduce inflation, it cannot be denied that we are beginning to feel the pinch of inflation everywhere
While we might be inclined to think that such issues are largely limited to less-developed countries, it will be inevitable that the issue of food insecurity will creep up on us if we continue with our current practices. As food price inflations continue to occur and food supply decreasing due to climate change, food insecurity will soon be a global issue.
But even though this situation does seem dire, it is a future that we can avoid if we do our parts!
How is Food Sustainability related to other forms of sustainability?
The importance of food sustainability also lies in its interconnections with other forms of sustainability, where according to the UN, the three key indicators of food sustainability are:
- Economic sustainability – the economy
- Social sustainability – the individuals within society
- Environmental sustainability – the climate and environment

Economic Sustainability: Sustainable food systems must be able to support economic growth (both locally & globally), creating jobs and long-term profitability in farming and food industries.
Economic growth also allows increased efforts towards developing better economically viable food sustainability strategies.

Social Sustainability: Social aspects of food sustainability include equal access to food supplies and education and job creation, and ethical labour practices within the food system such as production and distribution.
While food sustainability is important, it is also equally important to ensure that social inequalities are addressed to prevent the exploitation of individuals such as labourers.
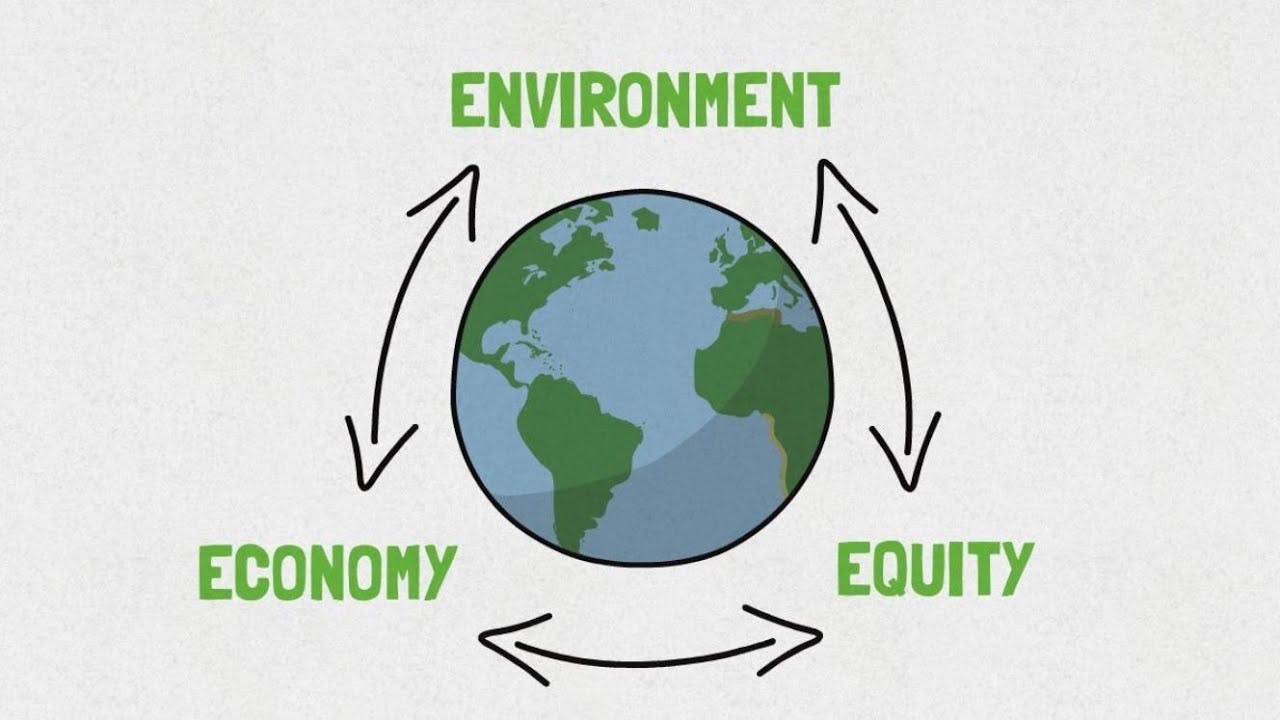
Environmental Sustainability: Sustainable food systems are essential in ensuring environmental health through the minimization of environmental damage and conservation of natural resources.
Current food systems contribute majorly to environmental harm through greenhouse emissions (accounting for almost ~30% of emissions) from activities such as transport and waste management.
So why does this matter to you?
Understanding these links allows you to make informed decisions that can contribute to sustainability.
For instance, supporting local businesses not only promotes local economic growth (economic) and creates job opportunities (social), but also reduces energy consumption during transport (environmental).
As such, knowledge and education are pivotal for creating change.
What is reaching Food Sustainability challenging?
The factors that influence food sustainability, range from environmental conditions to societal and economic considerations, and understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring food sustainability. Some key factors include:
- Climate change
- Agricultural constraints – land, farming methods
- Energy use – production, transport and storage
- Food waste management
- Access to education
Climate change
Did you know that one of the primary drivers of climate change is our agricultural practices? This impact on the climate was found to be the most prominent between the 1950s to 1970s, with rapid agriculture expansion causing massive greenhouse emissions.
And unfortunately, this negative impact on the environment has caused it to bite back – targeting our food security.
Heavy rainfall has resulted in soil erosion, preventing the proper growth of crops
From rising temperatures to droughts to the increased incidences of weather events, climate change has had adverse effects on our production of crops, including global staples such as soy, wheat and rice.
An agricultural study in West Africa, for instance, found that crop yields had dropped by ~6% from between 2005 to 2020. While this singular decrease of 6% might be little, a decrease in yield across multiple regions globally would have a significant impact on global food security.
"Agriculture is very sensitive to weather and climate, where it also relies heavily on land, water, and other natural resources that the climate affects."
The effects of climate change can often be mitigated through technological interventions (such as the usage of climate forecasting tools) or the implementation of more sustainable farming practices (including reduced chemical usage in farming).
These strategies, however, are largely limited by the lack of education or access to these tools.
Agricultural constraints
It has been estimated that over 38% of the global surface has already been dedicated to agricultural usage and with the growing demand for food due to rising populations, greater strain has been placed on the conversion of land for agriculture – a very unsustainable practice.
There is thus a need to develop interventions to maximize productivity while minimizing land usage.
"The farming methods accessible also have an impact on the sustainability of the farming practices in different regions. "
While sustainable methods like organic farming are ideal for the maintenance of environmental health to ensure sustainable food production, such methods are not always widely accessible – making it difficult to achieve global sustainable practices unless assistance is provided globally to achieve it.
Energy use
The energy usage in food production, transportation, and storage also influences sustainability significantly.
The reliance on fossil fuels for energy usage (such as long-distance transportation) contributes significantly to the greenhouse emissions that drive climate change – a major factor in food sustainability as mentioned above.
"Approaches to energy use management include transitioning to renewable energy sources (like solar and wind) or prioritization of local produce to reduce transportation distances, and thus carbon emissions."
These strategies, however, are again largely limited by the lack of education or access to these tools.
Food waste management
Food waste management is a major challenge in food sustainability, with an estimated one-third of food produced being either lost or wasted at every stage of the supply chain, from farms to households.
Methods to improve food waste management include the implementation of strategies to reduce food waste such as improving farming practices (such as the optimization of harvest times and methods) or the repurposing of food waste (such as upcycling).
"Upcycling can be done on an industrial to household level. Brands (like moonbeam.co) make use of food refuse like spent grains and upcycle them into edible treats. At home, you can also make use of waste such as vegetable scraps in a variety of ways."
Access to education
Access to education is another key limiting factor in working towards a sustainable future. As mentioned above, gaining knowledge and understanding is important in contributing to sustainability as you cannot make better choices if you don't know how to.
For instance, in rural agricultural regions, farmers are unlikely to be equipped with the knowledge or tools to implement sustainable practices like developed countries.
Research has even shown that farmers, themselves, sometimes might not be aware of issues such as climate change or the need for food sustainability – indicating a need to tackle the disparity in the knowledge accessible.
What Sustainable Practices can you adopt at home?
Being now well-equipped with knowledge on food sustainability, how then you can contribute to this effort? Here are some simple ways that you can go about it, beginning with:
#1 Supporting sustainable brands
When looking to go sustainable, you can start by supporting brands which go green through upcycling. As mentioned in our guide to upcycling, the act of upcycling is the process of breathing new life into food material which would have otherwise gone bad.
Common food materials often treated as waste include spent grains, soy okara and cacao husks.
"These food materials are often by-products of food production or processing processes. For instance, spent grains are produced during beer production using malt while soy okara is produced during soybean processing into soy products like soy milk."
As this process in turn also diverts food products away from landfills, upcycling aids in food production while reducing the environmental impact of food production.
And if you are afraid that these "wastes" are unsafe to eat, rest assured that they are completely safe and edible – being obtained from raw food products that you likely consume daily.
In Singapore, brands which upcycle that you can check out include:
- Confetti Snacks – vegetable chips from discarded vegetables
- the moonbeam co. – granola, cookies, bread from spent grains, coffee grounds
- Crust group – alcoholic beverages from food waste such as fruit peels, bread
- Mindful – non-alcoholic beverages from spent coffee ground
- PetCubes – nutritious ready-to-eat meals for both dogs and cats
If the world of upcycling interests you, read more about it here!
#2 Going local with purchases
Supporting local produce is another way to contribute to food sustainability, especially here in Singapore.
Red labels which you can look out for when doing grocery hunts that indicate local production in Singapore. More stars, in short, stand for greater sustainability and quality.
While the Singapore Food Agency (SFA) has increased efforts in supporting the agricultural sector to improve the amount of local produce, there needs to be an equally strong supporting consumer demand for these local produce – and that's where we come in.
Opting for local produce when shopping for kitchen supplies aids in food sustainability by:
- Reducing environmental impact – as less energy and resources are needed to store, transport or package produce for domestic travel as compared to international, the carbon footprint and emissions associated with the produce are lowered.
- Supporting local economies – promotes local economic growth and stability, ensuring jobs in the relevant fields. Supporting local economies also increases the robustness of our local food system, ensuring greater resilience to global food system disruptions (such as shortages).
Ps: If these "plus-points" sound familiar, it's because we talked about them in the earlier section – but you probably already know that – showing you the power of knowledge.
Look out for these red tags when shopping.
Our local produce can be found at supermarkets or the SG Farmers' Market, a partnership between SFA and the Singapore Agro-Food Enterprises Federation Limited (SAFEF).
And if you're looking to do online shopping, look no further than the e-SG Farmers' Market on Lazada. With many more options becoming available in recent years, it has never been easier to go sustainable.
Whether you're reading from Singapore or another part of the world, the benefits of going local are universally applicable, so let's support local together for our planet!
#3 Reducing food waste
Another way to lead a sustainable lifestyle at home is by reducing the food waste produced. Some ways to reduce food waste include:
- Meal planning
- Proper storage
- Repurposing food scraps
Meal planning is a simple solution to reducing food waste by limiting the amount of food kept at home.
By planning out meals for the week or coming weeks, you will be able to better gauge the amount of perishables you need when making purchases – reducing the likelihood of them going bad at home and going to waste.
And while this might take some getting used to, meal planning is a great way to also get healthy with your diet, allowing you to improve both your and the environment's health.
Even though good for your health together, you should avoid storing them in similar compartments to prevent quick spoilage of both
The proper storage of food is key in reducing food wastage, as correct storage methods can often significantly extend the shelf life of food.
For instance, vegetables and fruits while often stored together at home (like in my household), these produce should not be stored together as fruits (like tomatoes and apples) can emit natural gasses that speed up vegetable ripening, causing quicker spoilage.
Understanding the optimal conditions for storage (dry, warm, or cold environment etc.) is thus important in preventing food spoilage.
Repurposing food scraps such as vegetable scraps is also another creative way to breathe new life into your typical "waste" products – think of it as upcycling but in the comfort of your own home.
As previously shared, vegetable scraps can be used in a multitude of ways, ranging from using them to make soup broth and seasoning powders or even more interestingly, for re-growing entire vegetables.
If you're interested in finding out more about vegetable scraps, check them out here!
Conclusion
Hopefully, you now understand why it is important to be food sustainable and how we can implement some good practices into our day-to-day routine. Implementing new habits is always tough in the beginning so just pick one and move on from there – you don't have to do them all at once.
While our individual impacts might be small, I believe that if we all make the conscious effort to play our part and pass on these practices to future generations, the goal of a sustainable food system will not be far from our reach!
And on a side note, if you're interested in supporting food sustainability outside of your home and would like to collaborate with us, do shoot us an email (hello@themoonbeam.co) or drop us a message on our social media page.
We would love to have a chat and work together to support a common goal!